The Process
Informed by the principles of patient and public involvement, this resource was developed with the input of key expert groups in medication adherence-namely members of the public living with Multimorbidity (MM) and receiving polypharmacy, GP’s, practice nurses, pharmacists, psychologists, and learning technologists. A Collective Intelligence (CI) workshop was held to bring all of these experts together and to facilitate collaboration, idea generation, and the co-creation of design solutions.
The term ‘Collective Intelligence’ (CI) is used to describe intelligence that emerges as a result of a large number of people working together to come up with solutions to a difficult problem. The idea behind having a CI session is that a group of people working together can solve a problem more efficiently, and with more depth and insight, than any one individual could provide. As the individuals that were attending our workshop were all experts in medication adherence in different ways, we felt that a CI session was a very appropriate way of harnessing all of this knowledge and experience together.
Stage 1
The first stage of the CI process involved stakeholders generating a set of barriers in response to the following trigger question:
“What barriers do healthcare practitioners face in supporting people with multimorbidity who are taking multiple medications?”.
Stakeholders with expertise in relation to the problem context were contacted in advance of the session by email, with a request to respond to the above question. By email submission, experts identified 67 barriers, which were arranged into the following eight categories: Training and Education, Conflict, Communication, Ownership and Responsibility, Time Pressure, Resources and Support, Patient Behaviour and Abilities, Perspective. During the workshop, participants engaged in an analysis of the eight categories of barriers, with a view to generating options for overcoming barriers. In order to generate options in response to barriers, small working groups of participants (4-6 persons each) engaged in idea writing and discussion and, collectively, workshop participants addressed all eight barrier categories. Each of the small groups was asked to develop ideas and use open discussion to explore the meaning of those ideas. At the end of this process each working group orally reported the ideas generated in a plenary session. 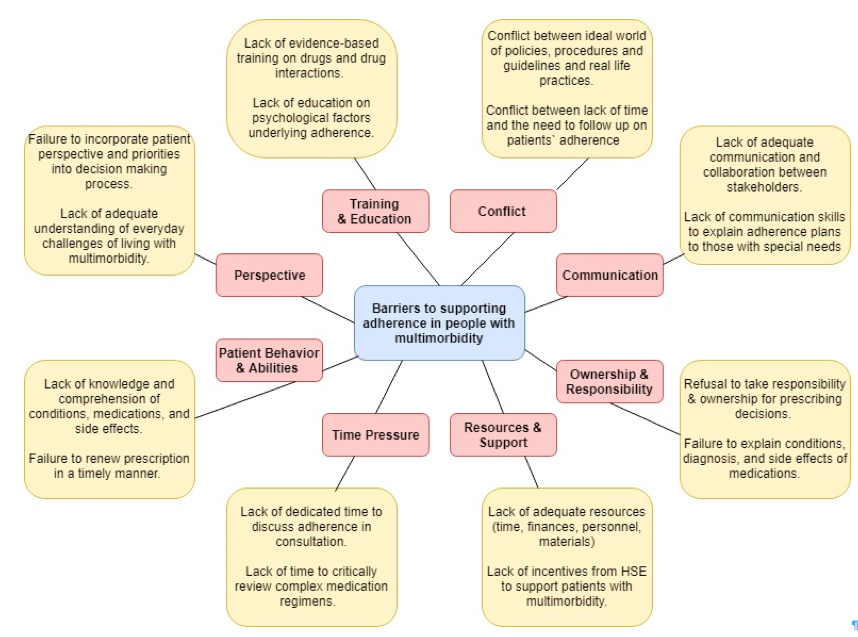
Figure 1; A sample of barriers within each category.
Stage 2
- Information and Knowledge Needs
- Communication Needs
- Decision-making Support Needs
- Behavioural Support Needs
- Relational Needs

Figure 2. Overview of needs generated in each category
Stage 3
After the CI workshop the facilitators combined all of the content that was generated from the day and produced a comprehensive report on findings and provided guidance on design considerations. Everyone that attended the workshop was sent a copy of this report and asked to provide feedback. The research team then engaged in deeper analysis of the full range of user needs highlighted by participants, with a view to prioritising the most important, impactful, and feasible needs to address in the first iteration of the e-learning system.
Once the content had been finalised and developed all stakeholders and everyone involved in the CI session were sent a link to the resource and invited to provide feedback which was then integrated in to this online package.
